Asalamualaikum ,
Here the one of the most of problem for people who like to play a tennis , but it not just play a tennis will cause this pain , it is related in our lifestyle and also one of the problem come when we always do a repetitive movement without notice we injured the ligament who are attached in our elbow.
Anatomy
of the Elbow
1.
Humerus
2.
Ulna
3.
Radius
What is Muscles that cross the elbow joint:
1.
Biceps
Brachii
2.
Brachialis
3.
Brachoradialis
4.
Triceps Brachii
5.
Pronator Teres, Supinator
6.
Wrist Flexors- Pronator Teres, Flexor Carpi
Radialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris, Palmaris Longus
7.
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, Extensor
Digitorum
8.
Wrist
Extensors- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus/ Brevis, Extensor Capri Ulnaris
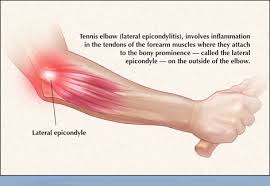
Tennis
elbow Definition
·
“A
pathologic condition of the common extensor muscles at their origin on the
lateral humeral epicondyle. Epicondylitis suggests an inflammation at one of
the epicondyles of the elbow.” (Dutton 419-22)
·
Tennis
Elbow generally occurs in adults between the ages of 35-50. It affects between
1%-3% of the population.(Dutton 419-22)
·
Tennis
elbow is typically an overuse injury. “Occupations or sports that involve
repetitive grasping, with the wrist in extension, place the elbow at risk
because it’s the wrist extensors that must contract during grasping activities
to stabilize the wrist.”(Dutton 419-22)
·
Leads
to tendonitis of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon.
What is
the symptom appears
1.
Diffuse
achiness
2.
Morning stiffness
3.
Occasional
night pain
4.
Dropping
of objects/ weak grip strength
5.
Pain
w/ palpation of lat. epicondyle
6.
Pain w/active or resisted extension
7.
Pain
w/ grasping objects with the effected hand (Dutton 419-22)
How to
trace it
Cozen’s
Test
·
“Resistive
Tennis Elbow Test: The patient sits with the examiner stabilizing the involved
elbow while palpating the lateral epicondyle With a closed fist, the patient—
pronates and radially deviates the forearm and extends the wrist against the
examiner’s resistance” (Sliker) A positive result would be if there is—
pain along the lateral epicondyle or objective muscle weakness
What are
physiotherapy Intervention Techniques
1.
Flexibility
exercises
2.
ROM exercises
3.
Stretching
4.
Active
assistive and resistive exercises
5.
Pain
Reduction with electrotherapy
6.
Tapping
and Braces
What are
our goal in treating the tennis elbow
1.
Decreased
pain
2.
ROM improved
3.
Joint swelling, inflammation, or restriction
reduced
4.
Muscle
performance increased
5.
Ability
to perform activities is improved
Home management and Treatment
• Rest •
Ice • Anti-inflammatories (aspirin, ibuproufen, voltaren gel/ fastum gel
What are
alternative treatment Intervention
1.
Deep
Friction Massage
2.
Acupuncture
3.
Bracing/ Splinting
4.
Cryotherapy
5.
Strengthening Exercises
6.
Stretches
7.
Surgery
8.
Exercises for Tennis elbow
From my experience in treating patient who had this problem i would like to say most properly
90% to 95% of people with tennis elbow had
been improve and recover with the treatment as above described. However, about
a few percentages as 5% of people will not get better with conservative
treatment and their will be refered back to the specialist for second opinion and
maybe need surgery to repair the injured
muscle-tendon unit around the elbow. Most of the patient who went for surgery, it results in pain relief and return
of strength after 2 month.
Wallahuaklam














0 Comments:
Post a Comment